OMEGA-3 fatty acids

1. What are omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega 3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids that are obtained from food and help in the development and maintenance of a healthy body.
Omega-3 fatty acids are classified into three categories:
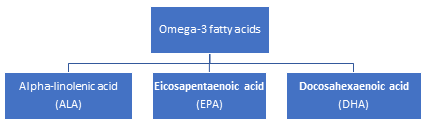
2. Why are omega-3 fatty acids so crucial for human health?
Omega-3 fatty acids provide materials for cell membranes (especially in the eye, brain and sperm cells) and protect the body from extreme temperatures.
Omega-3 fatty acids also provide energy to the body and protect internal organs (such as the heart, blood vessels, lungs, immune system and endocrine system).
3. What is the ideal amount of omega-3 fatty acids to consume?
Even though there is no official recommendation for omega-3 fatty acids, most health organisations agree that adults should consume 200–250 mg of combined EPA and DHA per day to stay healthy.
4. Which foods contain high sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are available naturally and can be found adequately from food sources like:
- Fish and other kinds of seafood (especially cold-water fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring and sardines)
- Nuts and seeds like flaxseed, chia seeds and walnuts
- Plant oils like flaxseed oil, soybean oil and canola oil
- Fortified foods such as eggs, yogurt, juices, milk, soy beverages and infant formula

Cod liver oil is a rich natural source of omega-3 fatty acids, including the nutrients EPA and DHA, which are essential for good health. It supports a healthy heart, vision and brain function, as well as strengthen the bones, teeth and muscles.
5. What are the different kinds of omega-3 dietary supplements available?
The major omega-3 dietary supplements are fish oil, krill oil, cod liver oil and algal oil, with algae being a vegetarian source. Omega-3 fatty acids are available in a wide range of dosages and forms.
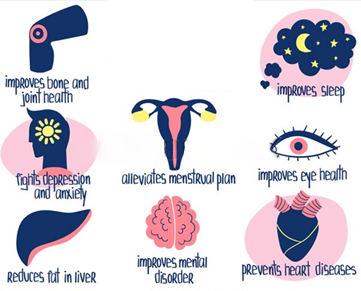
6. What are the roles of omega-3 fatty acids?
The roles of omega-3 fatty acids are as follows:
- May lower increased triglycerides levels in the body and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Also, work as an anti-inflammatory and may restrict joint pain and stiffness in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
- May also protect your skin from sun damage.
- May help in reducing menstrual pain in women who consume adequate amounts of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Can reduce liver fat and inflammation in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Improve the efficacy and tolerance of chemotherapy and may decrease the risk of some types of cancers like colon, prostate and breast cancer.
- Intake of higher amount of omega-3 fatty acids may help to reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). However, once diagnosed with AMD, taking an omega-3 supplement will not prevent the disease or decrease vision loss.
- The supplements of omega-3 fatty acids promote the brain development of a foetus during pregnancy and DHA supports brain development during infancy.
References
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Office of Dietary Supplements, US National Institutes of Health. 26 March 2021. Retrieved 10 June 2021.
- Essential Fatty Acids. Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University. 1 May 2019. Retrieved 10 June 2021.
- Omega-3 fatty acids. National institute of health. Available at: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-Consumer/#h7. Accessed 17 March 2022







